14 Apr Zebrafish Embryos: A Versatile and Affordable Animal Model for Scientific Research
As researchers in the field of developmental biology and animal modeling, We have discovered the advantages of using zebrafish embryos as an alternative to traditional animal models such as mice and rats. Zebrafish embryos are highly valuable due to their rapid development and manipulability. They offer researchers a host of advantages over other models including a high rate of reproduction, transparency, small size, and affordability.
One of the greatest advantages of zebrafish embryos is their highly rapid development. Organogenesis typically occurs within 48 hours of fertilization and fish are fully developed and swimming around 5-6 days post fertilization, providing a convenient model for observation during High Content Screening (HCS). Additionally, zebrafish breed year-round and females produce hundreds of eggs on a weekly basis, resulting in a very low cost per assay compared to mice.
Another key advantage of zebrafish embryos is their transparency. Embryos and the chorion are almost 100% transparent, allowing researchers to easily observe early development and effects of test compounds on developing bodily systems non-invasively. This transparency also makes zebrafish embryos highly permeable to small compounds which are added to the water environment and diffuse freely into the embryo.
Zebrafish embryos are also highly versatile in terms of research areas. From vertebrate developmental biology and transgenic research to toxicology assays, zebrafish embryos are one of today’s leading in vivo animal models. Zebrafish have orthologs in 82% of human disease-associated genes, making them especially translatable for genetic research. Human genes which have been sequenced to find mutations are identified and ‘knocked-out’ in zebrafish to mimic the disease environment. These transgenic, transparent zebrafish embryos can be monitored for changes in their neurological, musculo-skeletal, and organ systems. Advances in the understanding of diseases such as melanoma, muscular dystrophy, and kidney afflictions have been particularly successful.
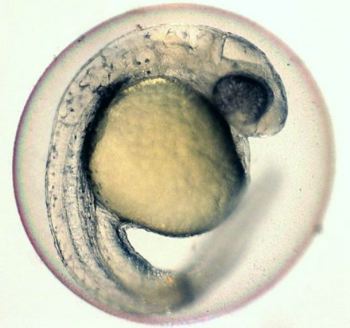
Zebrafish embryo (Photo: University of Guelph).
In preclinical studies using High Content Screening (HCS) of small molecules, zebrafish embryos provide a method of quickly assessing toxicity and efficacy of new drugs. This saves both time and money in the very expensive process of Drug Discovery. In recent years zebrafish embryos have become a prominent model for the early development of new drugs in toxicology, cancer research, human genomics, developmental biology, and other fields.
Finally, the use of zebrafish embryos as models at 5 days post fertilization adheres to the 3Rs of Animal Research (Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement) and greatly reduces the use of mammals in later stages of research. Zebrafish embryos offer an affordable, effective, and more humane alternative to traditional animal models.
In summary, zebrafish embryos are uniquely suited to a wide range of genetic and toxicology studies. Their rapid development, transparency, small size, and genetic similarities to humans make them a first-rate whole-organism model. In cases where in vitro models do not suffice, and in vivo models like mammals don’t meet regulations, zebrafish embryos offer an affordable, effective, and more humane alternative.
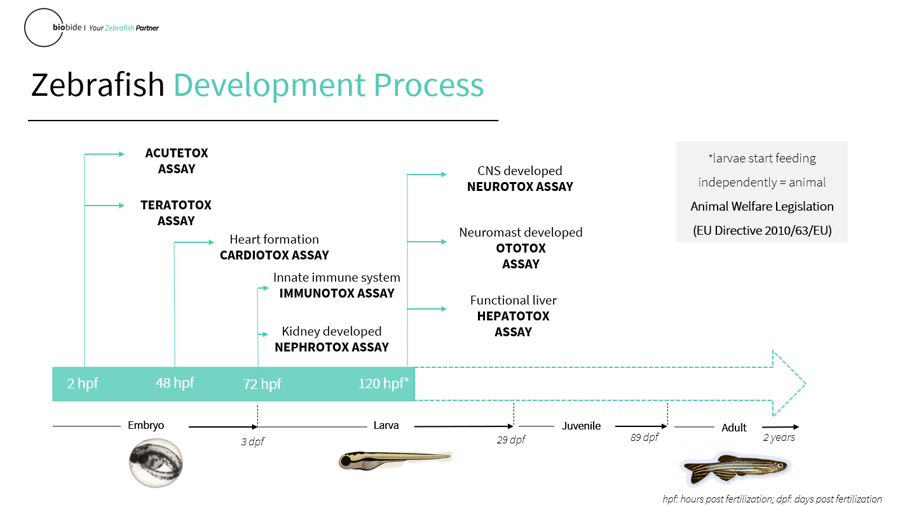
Source: https://blog.biobide.com/how-can-zebrafish-embryos-be-used-as-an-animal-model.



No Comments