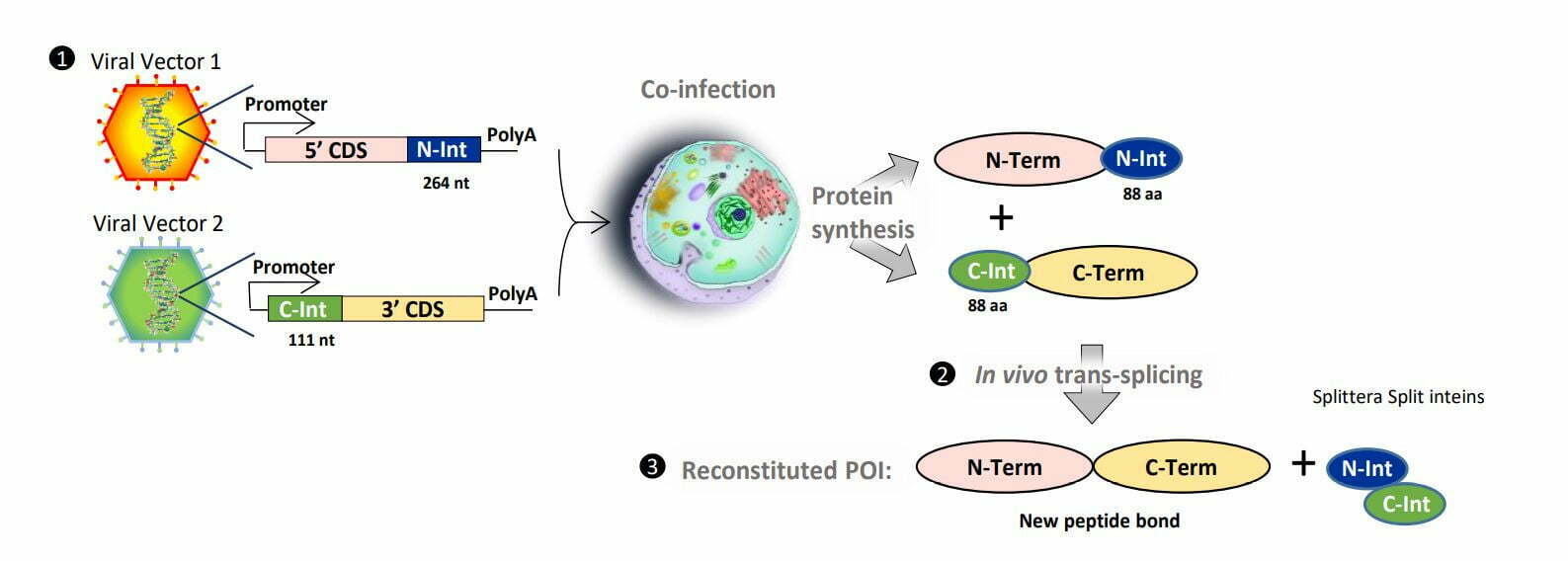
SPLITERA is a versatile protein engineering tool that allows the conjugation of proteins through the formation of new peptide bonds. This technology address the main limiting factors in Gene Therapy. It overcomes gene size limitations of viral vectors, allowing the covalent reconstitution of large proteins expressed by different viral vectors in vivo. Moreover, it allows virus surface modification to target viral particles to specific tissues.
SPLITTERA overcomes gene size limitations of viral vectors, allowing the covalent assembly of large proteins expressed by different viral vectors in vivo through Intein mediated trans-splicing reaction. Recent work demonstrate that inteins are applicable to genes related to inherited and non-inherited diseases1 and to deliver highly efficient base editors .
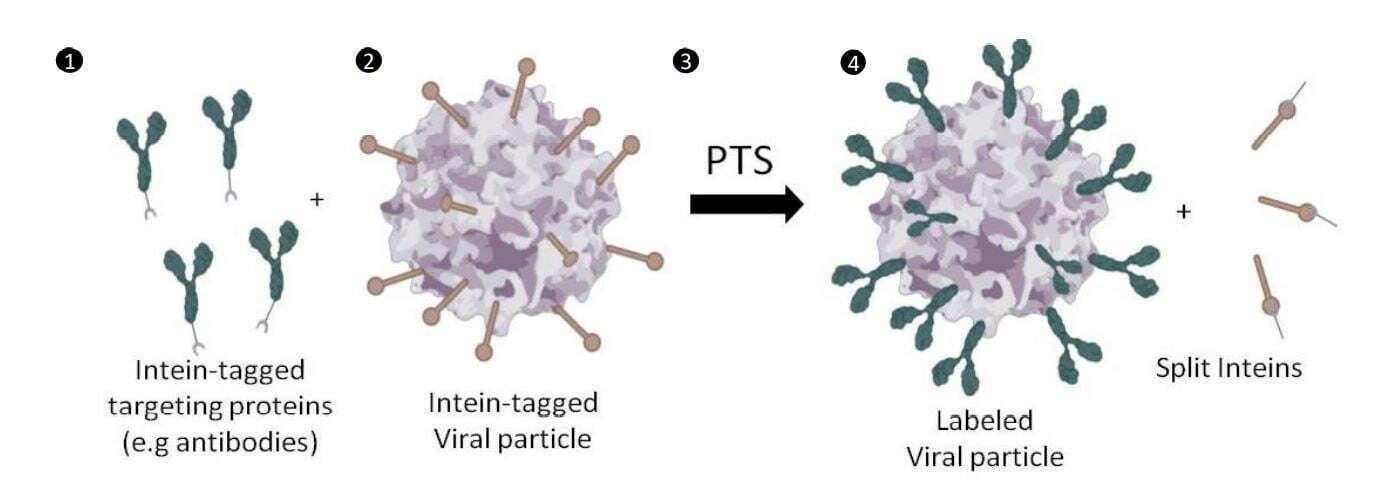
SPLITTERA Split Inteins mediate the covalent display of targeting proteins on the surface of a virus. Targeted viral particles allow restricted and tissue specific gene delivery.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 11 months | Cookie from Google Inc. to collect web statistics. No personal user data is collected. |
| _ga_******** | 11 months | Cookie from Google Inc. to collect web statistics. No personal user data is collected. |
| _gid | 11 months | Cookie from Google Inc. to collect web statistics. No personal user data is collected. |

