31 Mar Fluorescent Transgenic Zebrafish: A Versatile Tool for Drug Screening and Discovery
Transgenic Zebrafish have become an increasingly popular tool for researchers looking to identify human disease-related mutations and the drugs that treat them. This article will focus specifically on fluorescent transgenic Zebrafish lines and how they can be used in drug discovery and development.
Advantages of Fluorescent Zebrafish in Drug Screening
Despite the apparent differences between Zebrafish and humans, there is sufficient homology in biochemical pathways and organ structures between the two. Zebrafish have orthologs in 80% of human disease-related genes, and their genes are easily manipulable. Additionally, the embryonic and larval stages of Zebrafish offer advantages such as external development and fertilization, embryo transparency, and rapid organogenesis. These features make Zebrafish ideal for expressing fluorescent proteins to mark a concrete target or organ for image analysis.
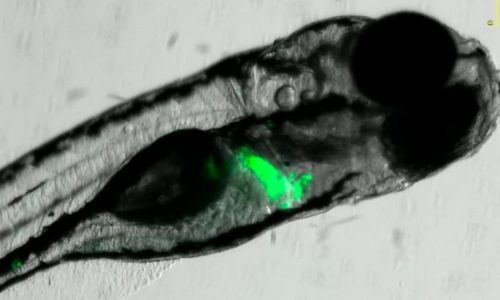
Application of Fluorescent Transgenic Zebrafish Lines
The transparency of zebrafish embryos allows for the use of fluorescent proteins in analyzing the potential toxicity of pharmacological, agrochemical, and cosmetic compounds. Additionally, fluorescent transgenic zebrafish lines can be used to study the efficacy of new drugs.
Toxicology Assays
Fluorescent zebrafish lines are well suited for studying the toxicity related to specific organs through image analysis. Analysis can be done both qualitatively and by quantifying the fluorescence. One of the most commonly used proteins is GFP, which generates a green fluorescence, and mCherry, which generates a red fluorescence.
Cardiotoxicity
Cardiotoxicity is a major threat to human health, especially during heart development in the early stages of life. Zebrafish hearts are very similar to human ones, and the use of green fluorescence in the heart allows researchers to track heart function and identify functional alterations such as arrhythmias or atrioventricular failures. Researchers have found that drugs producing cardiac toxicity in humans usually reproduce bradycardia or a 2:1 arrhythmia in zebrafish embryos, which can be analyzed in a High Content Screening (HCS) platform, increasing the efficiency of pre-screening assays.
Hepatotoxicity
Transgenic zebrafish with fluorescence in the liver can be used to visualize and identify liver cells by image analysis, making it easier to identify the whole area of the liver.
Nephrotoxicity
Fluorescent zebrafish are increasingly used to analyze kidney function due to their similarities to humans. Transgenic zebrafish with fluorescence in the kidney helps to visualize the organ better and detect malformations of the glomerulus or the tubules.
Efficacy Assays
Several neurodegenerative and neuromuscular zebrafish models have been created and can be used for target validation and to screen potential drugs to treat these diseases. These diseases include Parkinson’s Disease, Alzheimer’s Disease, Epilepsy, and Huntington’s Disease.
In conclusion, fluorescent transgenic zebrafish lines are a powerful tool in drug discovery and development. They offer researchers the ability to track specific organs and cells, making it easier to detect malformations and assess potential toxicity of compounds. Additionally, they can be used to study the efficacy of new drugs, particularly in rare diseases affecting a small number of people.



No Comments